Turbulent Flow
Turbulent flow, which involves eddy currents, occurs only in larger leaks and at higher pressure differences. With a high speed of gas, only leaks with turbulent flow emit a sound (whistle) and these can be searched with ultrasonic leak detectors.
The formula for the leakrate at turbulent flow is not given here since leaks with turbulent flow are so large and can be readily located and repaired. There is seldom a need for calculation.
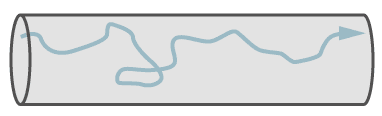
Path of a single molecule in turbulent flow.