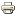
Viscosity of some gases
Type of Gas
Air
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Argon
Hydrogen
Helium
Carbondioxide
R-12
R-22
R-134a
R-600a
Formular
N2
O2
Ar
H2
He
CO2
CCl2F2
CHClF2
CH2F-CF3
CH(CH3)2-CH3
Viscosity at 15°C in Pa·s
18.0 · 10-6
16.3 · 10-6
19.9 · 10-6
22.0 · 10-6
8.7 · 10-6
19.4 · 10-6
14.5 · 10-6
11.6 · 10-6
12.0 · 10-6
11.61 · 10-6
7.4 · 10-6
As one can see, the difference of viscosity between gases is not so large, all are in the same order of magnitude.